Food preservation has been one of the most important needs of people since settled life. The foods in the period of hunting and gathering in human history were consumed before spoiling, but the products had to be kept between the two harvest periods after the agricultural production started. Likewise, meat, fish, and dairy products should be kept for a certain time.
In ancient times, methods such as storage, salting, smoking, burying, cooking, drying, and canning were used in cold caves by trial and error in order to preserve food. Thus, food is protected without spoiling until consumption. Today, the cold chain is used to meet this need.
Microorganisms, enzymes, temperature, and light are the leading causes of food spoilage. When microorganisms meet the appropriate comfort conditions on foods, they quickly consume nutrients and make food that should be beneficial harmful. The cold chain is a system cycle that prevents chemical, biological and microbiological effects that can occur with food spoilage. In short, it is the path from the manufacturer to the table of the consumer. It is also one of the most important parts of food safety. In order to ensure food safety, the cold chain should not be broken during the storage, packaging, shipment and display stages of the products.
If we briefly summarize the cold chain as an image, it is as follows.
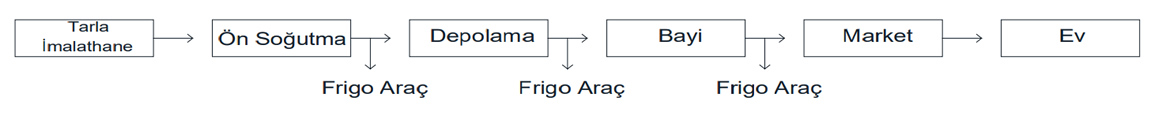
Pre-cooling is the process of gradually lowering the core temperatures of the fruits and vegetables collected from the field to the storage temperature. Subjecting post-harvest pre-cooling prevents microorganisms to grow, thus extending the storage period and preventing their appearance from deteriorating. After the pre-cooling process, some products are offered for direct marketing, while some products are taken to cold storage. The products taken to the cold storage without the pre-cooling process change the structure of the products in the cold storage as they change the temperature. There are also pre-cooling with forced airflow, hydro cooling with water, pre-cooling with snow or flake ice, vacuum pre-cooling. The selection criteria of these methods vary according to the product to be cooled.
Quick Freezing (shocking) is the rapid lowering of the temperature of their products. Shocking is mandatory for products to be stored at -18 ˚C. In the pre-cooling process, some products brought to a temperature of 0-5 ˚C are taken to the freezing chambers before being taken to frozen storage storages, and this section, called the freezing tunnel, is set as the core temperature of –18 ˚C. Product freezing methods such as compressed air flow (forced air) shocking, plate freezers, brine shocking are available.
Products taken to storage rooms after pre-cooling and freezing processes. It is preserved there until the next consumption time and becomes more valuable in the market. Different methods are used today for the preservation of food. The most important of these methods is the cold application method that we use in almost every field today. Cold storages formed by the inhibition of the growth and activities of microorganisms, which also contain foods at low temperatures, can be examined under 2 main headings. The first of these is the cold storage where the products consumed in a short period are kept, usually, the fruits and vegetables are stored, and the other one is the long-term storage, usually frozen storage rooms where meat and dairy products are stored.
Cold storages are where products are stored at 0 ° C or a few degrees higher. It is not correct to give a constant temperature value since the degree of storage varies according to the product. In cold storage, the humidity has an important place besides temperature. In other words, the temperature, the humidity and the endurance period are different for each product. For this reason, the capacity and dimensions of the cooling machine and installation to be made in the cold storage vary according to the preserved product.
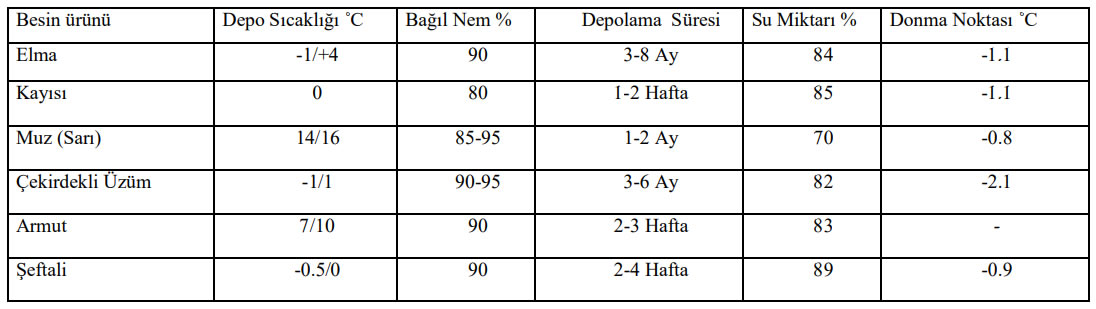
Frozen storage is the storage of products taken from freezing chambers at -18 ° C and below. Fruits and vegetables contain freezing water, and by converting this water into ice, the water activity of the products is reduced. The lowering of the temperature along with water activity reduces the speed of chemical and biochemical reactions and microbial activities. Temperature and humidity differ in the product, in frozen storage as well as in cold storage.
Products are put into frozen storage rooms in small packages, such as going directly to the sale, and products are also placed in large boxes for later packaging. The storage of the products can be done with special shelf systems or with the help of pallaxes to heights that exceed the length. When the products are needed to be consumed, the products are taken from the storage rooms to the processing areas at 12 ˚C.
After packaging of the products, they are loaded on the refrigerated vehicles and delivered to the consumption area. Different thicknesses and different vehicle air conditioners are attached to the refrigerated vehicles according to the storage temperature, so the products are transported at the storage temperature. While special fan cooling systems are used for +4 ˚C and -18 ˚C refrigerated vehicles, the charging method is used with the help of eutectic plates for -25 ˚C vehicles. These vehicles are mostly used in ice cream shipment. Refrigerated vehicles are not for the cooling of the product, but for the shipment of the product at the storage temperature. The products shipped with the refrigerated vehicles are taken to the display cabinets or deep freeze cabinets without breaking the cold chain, here they wait for the day when the end consumer will go to their cabinets.

